
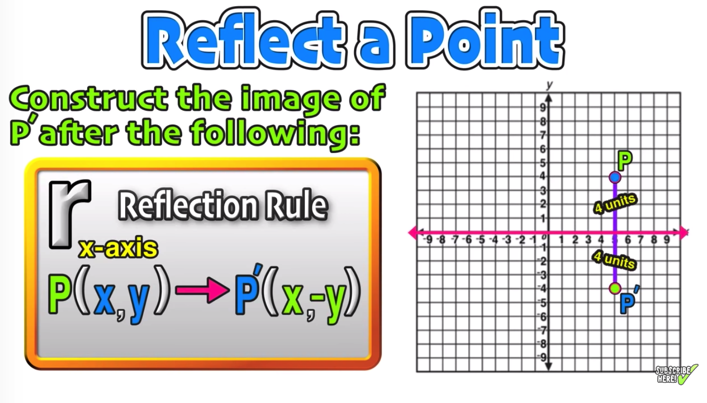
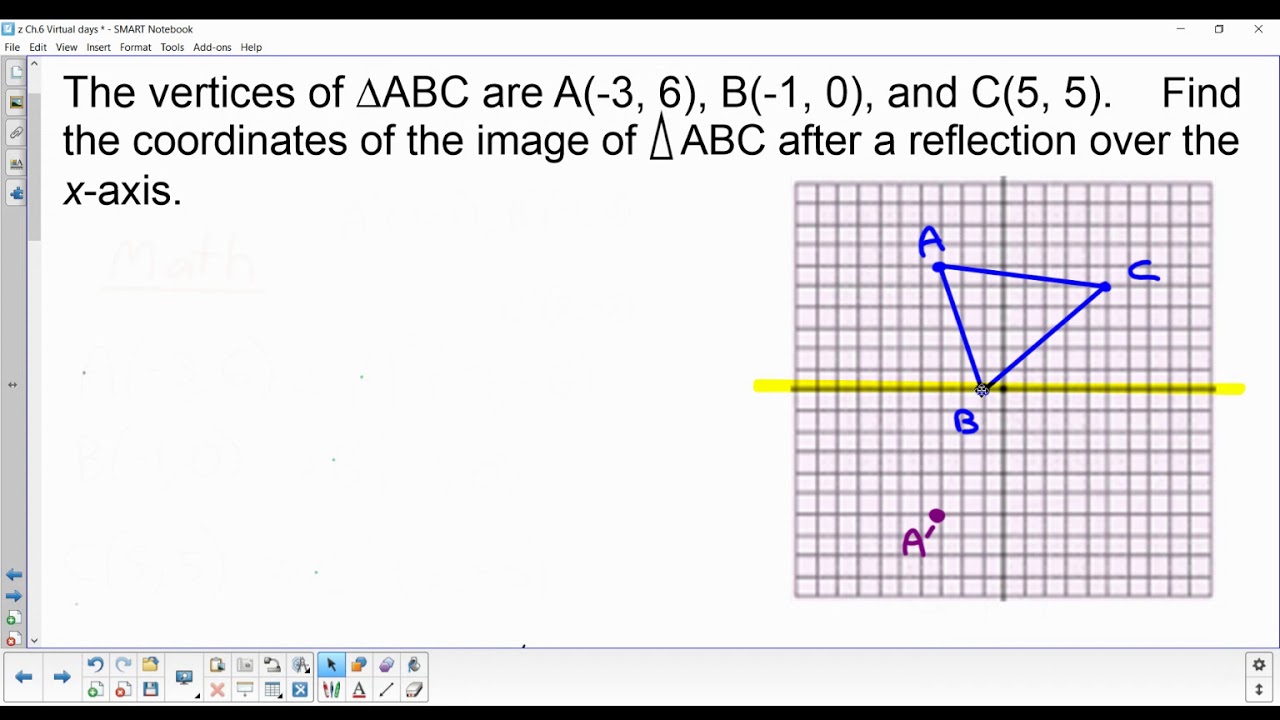
The -coordinate remains the same when a point is reflected across the -axis, while the -coordinate is turned into the opposite (its sign is changed). What happens to the coordinate when a point is reflected? Therefore, the reflection of the point (x, y) across X-axis is (x, -y). But the Y-coordinates are transformed into its opposite signs. When a point is reflected across the X-axis, the x-coordinates remain the same. The reflection transformation may be in reference to X and Y-axis.
What happens when a point is reflected on the x axis? These reflected points represent the inverse function. Reflection Across Y=X When reflecting over the line y=x, we switch our x and y. If a point is on the line of reflection then the image is the same as the preimage. The line of reflection is the line that a figure is reflected over. When a point or shape is flipped across a line creating a mirror image?Ī reflection is a transformation that turns a figure into its mirror image by flipping it over a line. If you reflect over the line y = -x, the x-coordinate and y-coordinate change places and are negated (the signs are changed).
When you reflect a point across the line y = x, the x-coordinate and y-coordinate change places. What is the rule for a reflection over the line y x? How do you know if it’s a reflection in the x or y-axis?Ī vertical reflection reflects a graph vertically across the x-axis, while a horizontal reflection reflects a graph horizontally across the y-axis. For example, as you can see in the image, the triangle in the mirror is flipped over compared with the real triangle. That something is the new shape’s orientation. When you reflect a shape in coordinate geometry, the reflected shape remains congruent to the original, but something changes. When a figure is reflected What stays the same? The only difference is that, rather than the y-axis, the points are reflected from above the x-axis to below the x-axis, and vice versa. Reflection across the x-axis: y = − f ( x ) y = -f(x) y=−f(x) The concept behind the reflections about the x-axis is basically the same as the reflections about the y-axis.
What does it look like when a function is reflected across the x-axis? The rule for a reflection over the x -axis is (x,y)→(x,−y). What is the rule for a reflection over the x-axis?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
